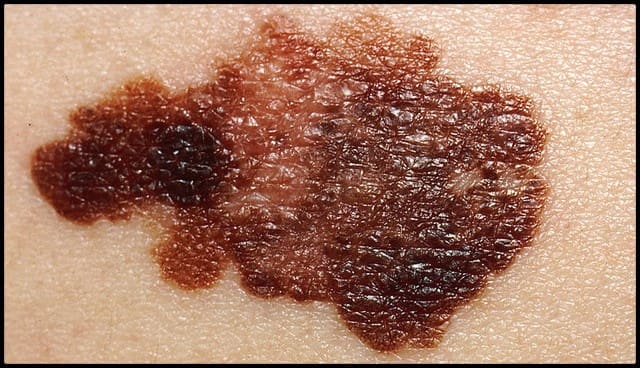
Malignant Melanoma
The overall number of malignant melanoma cases continues to rise, now becoming the most common form of cancer in young adults aged 25 to 29 and the second most common cancer in adolescents and young adults aged 15 to 20.
Advanced melanoma can spread to your lymph nodes and internal organs, becoming fatal if not taken care of. In fact, there is one person to die every hour in the United States from melanoma. Fortunately, if melanoma is detected early on and treated before it can reach the lymph nodes, the survival rate increases to 99%.
The risk factors for developing malignant melanoma include a family history, having a history of severe sunburns, atypical nevi, skin that easily burns, freckles, doesn’t tan easily, having naturally blonde or red hair, or having blue or green eyes. While some of these statistics may seem crazy, they have been proven true.
Environmental factors are also important, such as living at a high altitude or in an extremely sunny climate, being exposed to sunlight often, or using tanning beds.
Related Pages
Quick Quote
How Dangerous is Malignant Melanoma?
When detected early on and treated properly, malignant melanoma is usually curable. However, once it has spread into deeper layers of the skin and other parts of the body, it can become more difficult to treat and can even be deadly. When it is detected early, the estimated five-year survival rate for patients in the United States is around 99%. But research has found that an estimated 6,850 people in the United States will die from melanoma in 2020.
Different Types of Malignant Melanoma
There are four main types of malignant melanoma of the skin, each type varying based on your risk factors and the severity of the condition.
Superficial Spreading Melanoma
This is the most common type of melanoma to be diagnosed among patients. It can live in an existing mole or appear as a new lesion on your skin. When it starts in an existing mole, it tends to grow on the surface of your skin for quite some time before going any deeper. And while it can appear anywhere on the body, it’s most likely to show up on the torso of men, legs of women, and the upper back of both. You should keep an eye out for any flat, slightly raised, or discolored, asymmetrical patches that have uneven borders. Their colors vary from tan, to black, brown, red or pink, blue, or even white.
Lentigo Maligna
This form of melanoma develops most often in older people. When it becomes invasive or spreads beyond its original site, it becomes known as lentigo maligna melanoma. At first, this type of cancer will grow close to your skin’s surface, typically on sun-damaged skin, the face, ears, arms, or upper torso. It will also appear as a flat or slightly raised, blotchy patch that has uneven borders. Its colors range from blue and black, to tan, brown, or dark brown.
Acral Lentiginous Melanoma
This type of melanoma is most often found in African Americans. It can be harder to find as it usually shows up in places such as under your fingernails, on the soles of your feet, or the palms of your hands. Depending on its severity and location, it could appear as a black or brown area.
Nodular Melanoma
This is the most aggressive form of malignant melanoma. It can account for 10 to 15 percent of all melanoma cases. The tumor will grow deeper into the skin and more rapidly than any other form, frequently found on top of the torso, legs, arms, and sometimes the scalp of other men. More often than not, by the time it is found and diagnosed, it is already invasive. This form of melanoma is often recognized as a bump that appears on the skin, often black or blue in color, but not uncommon to appear pink or red either.
Malignant Melanoma Symptoms
Melanomas can develop almost anywhere on your body, most often in the areas that have been exposed to the sun, such as your back, legs, arms, or face. They can also appear in areas that aren’t as exposed to the sun, like your feet, hands, or fingernail beds. However, these hidden melanomas are most common among people who have darker skin.
The first signs of developing melanomas can vary; however, the most common symptoms include those we’ve listed below.
- Changes in an existing mole
- New pigmented or unusual growths on your skin
Possible Causes for Malignant Melanomas
One of the most common causes for melanomas is when a mistake happens within the melanin-producing cells that give your skin its color. Normally, skin cells will develop in a controlled process where healthy cells push older ones towards the skin’s surface. However, sometimes these cells develop DNA damage, making the new cells develop uncontrollably and cause a mass of cancerous cells.
It isn’t exactly clear what DNA damages lead to melanomas, but it’s likely that it is a combination of factors, including environmental and genetic factors. No matter what these factors are, doctors still believe that UV exposure and tanning beds are the leading cause of melanomas.
Diagnosing Malignant Melanomas
There are several tests and procedures that can be taken to diagnose melanomas; however, there are two common procedures that are almost always right.
- Physical Exams – If you go for a physical exam at your physician’s office, your doctor will ask you questions about your history and examine your skin for any possible melanomas.
- Biopsy – A biopsy is when a tissue sample is removed for testing. This type of test will determine whether the lesion is a melanoma or something else. The type of biopsy procedure recommended by your doctor will depend on your situation. While most doctors will recommend having the growth removed when possible, others will conduct a punch biopsy. This is where a circular blade is pressed into the skin around the suspicious mole or lesion.
Treatment Options for Malignant Melanomas
The best treatment course for your melanoma will depend on the size and location of your cancer, your current health, and of course, personal preferences. Treatment options for smaller cancers usually include removing the entire melanoma; however, if the cancer is larger or has spread, there are other available options.
- Surgery – If the cancer has spread to your lymph nodes, your doctor might recommend going ahead and removing the lymph nodes.
- Immunotherapy – This treatment options is a drug that helps your immune system to fight off the cancer. It is often recommended after surgery, especially when the entire melanoma cannot be removed with surgery.
- Targeted Therapy – Targeted drug treatments focus on specific weaknesses that are present within cancerous cells. By targeting those weaknesses, it can cause the cells to die off. The cells from the melanoma will need to be tested to see if targeted therapy will be a good source of treatment against your cancer.
- Radiation Therapy – This type of treatment uses high-powered energy beams, such as protons or X-rays, to kill your cancerous cells. It can be directed to the lymph nodes if your cancer has spread there; however, it can also be used to treat melanomas that surgery can’t remove.
- Chemotherapy – Chemotherapy utilizes drugs to kill off your cancerous cells. It can be given to a patient intravenously, in pill form, or both ways to ensure it reaches the melanoma. It can also be given to you in a procedure called isolated limb perfusion; this is where blood isn’t allowed to circulate to certain areas of the body so the chemotherapy can reach the cancer directly.
What You Can Do?
Whether you’re at high risk of developing cancer, if your family has a history of cancer, or if you simply want to be cautious, there are several steps you can take at home to check for melanomas. There are also steps you can take to prevent any new melanomas from developing.
- Check Yourself – At least once or twice a month, give yourself a head-to-toe check for any new blemishes or growths on the skin. If you find any new moles or any that may look suspicious, contact your dermatologist.
- See Your Dermatologist – No matter if you’ve found a new, unusual growth on your skin, or if you simply wish to have an exam, you can always seek guidance from your dermatologist.
- Follow Up Regularly – Even if you haven’t found an unusual blemish on your skin, having regular visits with your dermatologist is important. We recommend having these visits at least once a year if you don’t find a new blemish or growth.
Why Choose Winston Salem Dermatology?
It’s important that you always take care of your skin, especially if you’ve experienced skin cancer in the past. But it’s just as important to make sure you have a dermatologist you can trust and rely on. You can contact us today at (336) 774-8636 to set up an exam or to simply learn more about our products and services. Your skin and your health is our passion here at Winston Salem Dermatology.
Related Pages
Quick Quote
Address
Winston Salem Dermatology & Surgery Center
1400 Westgate Center Drive,
Suite 200 - Winston Salem, NC 27103
Phone: 336.774.8636
Fax: 336.774.0265
www.WinstonSalemDermatology.com